
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, data is an invaluable asset for organizations of all sizes. With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, implementing robust Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies has never been more essential. Consequently, DLP encompasses a variety of tools and practices designed to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, loss, or theft. This comprehensive guide will explore effective DLP strategies, their importance, and practical steps for implementation.
Understanding Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
What is DLP?
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) refers to a collection of strategies and tools designed to prevent sensitive information from being lost, misused, or accessed by unauthorized users. As a result, DLP solutions monitor, detect, and respond to potential data breaches, ensuring that crucial information remains secure.
Importance of DLP in Cyber Security
1. Regulatory Compliance
Organizations across various industries are subject to stringent regulations regarding data protection. Therefore, non-compliance can lead to severe financial penalties and reputational damage. Thus, DLP strategies help ensure compliance with laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS by effectively protecting sensitive data.
2. Reputation Management
Moreover, a data breach can significantly harm a company’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and revenue. By implementing strong DLP measures, organizations can protect their data and maintain a positive public image. Consequently, this builds customer loyalty and trust.
3. Financial Protection
Additionally, the financial repercussions of a data breach can be devastating. Costs may include legal fees, regulatory fines, and loss of business. Hence, DLP strategies help mitigate these risks, thereby safeguarding financial health.
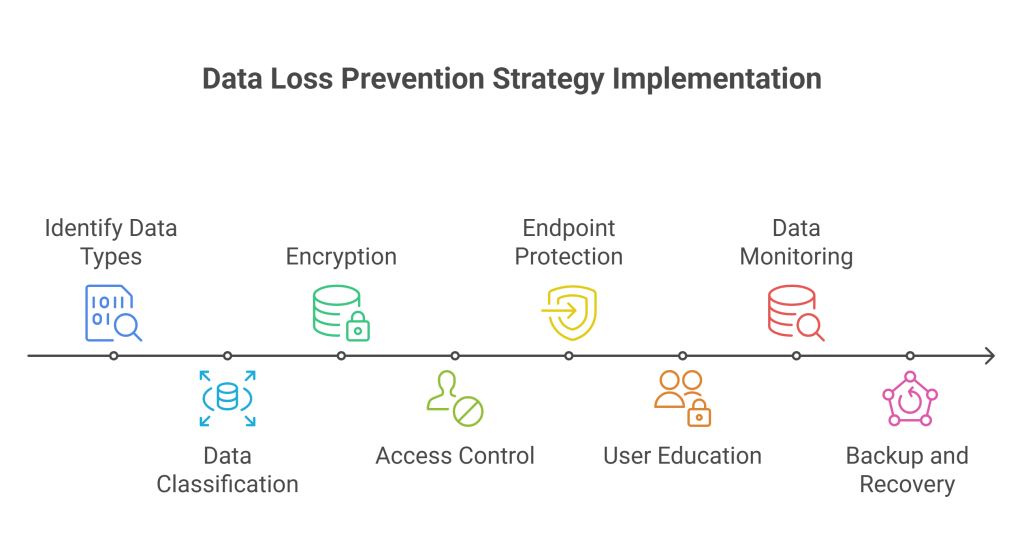
Types of Data to Protect
Identifying the types of data that require protection is crucial for developing an effective DLP strategy. Common categories of sensitive data include:
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): This includes information that can be used to identify an individual, such as names, addresses, and social security numbers.
- Financial Data: Banking information, credit card numbers, and financial records fall into this category.
- Intellectual Property: Trade secrets, patents, and proprietary designs are also critical.
- Health Information: Medical records and health insurance details require protection as well.
Key DLP Strategies
1. Data Classification
Data classification is the foundational step in establishing a DLP strategy. By categorizing data based on its sensitivity, organizations can prioritize protection efforts more effectively.
Implementation Steps:
- Develop a Classification Framework: Create categories such as public, internal, confidential, and restricted to apply appropriate security measures. This categorization is essential for clarity.
- Label Data: Utilize metadata tagging to ensure that employees are aware of the sensitivity of the data they handle. This step is vital for maintaining data integrity.
2. Encryption
Encryption is a critical component of any DLP strategy. It protects data at rest, in transit, and during processing, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. Therefore, implementing strong encryption is crucial.
Implementation Steps:
- Use Strong Encryption Standards: Implement AES-256 or similar encryption standards for sensitive data. This enhances security significantly.
- Encrypt Data in Transit: Utilize Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure data during transmission over networks. Consequently, this prevents interception.
3. Access Control
Restricting access to sensitive data is essential for preventing data loss. Implementing access control measures ensures that only authorized personnel can access critical information.
Implementation Steps:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on job roles and responsibilities to minimize the risk of unauthorized access. This approach is effective in limiting exposure.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic audits of access logs to identify any unauthorized access attempts or anomalies. This is vital for maintaining oversight.
4. Endpoint Protection
Endpoints, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, are often vulnerable to data breaches. Thus, implementing endpoint protection measures is crucial for safeguarding data on these devices.
Implementation Steps:
- Install Security Software: Utilize antivirus and anti-malware solutions on all endpoints to detect and prevent malicious attacks. This helps in proactive defense.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): Employ MDM solutions to enforce security policies on mobile devices, ensuring that sensitive data is protected. Consequently, this limits exposure.
5. User Education and Awareness error is a leading cause of data breaches. Therefore, educating employees about data security best practices is vital for the success of a DLP strategy.
Implementation Steps:
- Conduct Regular Training: Offer training sessions that cover topics such as phishing awareness, safe data handling, and password management. This empowers employees to be more vigilant.
- Promote a Security Culture: Foster a culture of security within the organization, where employees feel responsible for protecting sensitive information. As a result, this enhances overall security.
6. Data Monitoring and Incident Response
Continuous monitoring of data access and usage is vital for identifying potential data breaches. An effective incident response plan ensures that organizations can react swiftly to mitigate damage.
Implementation Steps:
- Implement DLP Tools: Use DLP solutions that provide real-time monitoring and alerts for suspicious activities. This allows for immediate action when needed.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: Create a plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a data breach, including communication protocols and mitigation strategies. This preparation is essential.
7. Backup and Recovery
Regular data backups are essential for ensuring that sensitive information can be restored in the event of a breach or data loss. Thus, having a solid backup strategy is critical.
Implementation Steps:
- Automate Backups: Utilize automated backup solutions to ensure that data is regularly backed up without manual intervention. This reduces the risk of human error.
- Test Recovery Procedures: Regularly test data recovery procedures to ensure that backups can be restored quickly and effectively. Consequently, this minimizes downtime.
Advanced DLP Techniques
1. Data Loss Prevention as a Service (DLPaaS)
With the rise of cloud computing, many organizations are turning to Data Loss Prevention as a Service (DLPaaS). This approach allows businesses to leverage cloud-based DLP solutions that are scalable and easy to manage.
Benefits of DLPaaS:
- Scalability: Easily adjust resources based on the organization’s needs. Therefore, this flexibility is advantageous.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure, which can be expensive. This makes DLP more accessible.
- Expert Support: Access to specialized security expertise without the need for in-house resources. This is particularly beneficial for small organizations.
2. Machine Learning and AI in DLP
Integrating machine learning and artificial intelligence into DLP strategies can enhance threat detection and response capabilities. These technologies can analyze patterns in data usage and identify anomalies that may indicate a potential breach.
Implementation Steps:
- Deploy AI-Powered DLP Solutions: Use tools that incorporate machine learning algorithms to improve detection rates and reduce false positives. This innovative approach enhances security.
- Continuous Learning: Ensure that the AI systems are regularly updated with new data to adapt to emerging threats. This adaptability is crucial for effectiveness.
3. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions provide advanced monitoring and response capabilities for endpoints. Integrating EDR with DLP strategies can enhance overall data protection.
Benefits of EDR:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides continuous surveillance of endpoint activities, allowing for immediate detection of suspicious behavior. This significantly enhances security.
- Automated Response: EDR solutions can automatically respond to threats, limiting potential damage. Thus, this reduces response times and protects data.
Case Study: Successful DLP Implementation
Company Overview
InnovateTech is a startup in the software development sector that faced significant challenges in protecting sensitive customer data. After experiencing a minor data breach, the company recognized the need for a comprehensive DLP strategy.
DLP Implementation Steps
- Data Classification: InnovateTech categorized its data into sensitive and non-sensitive categories, focusing on customer financial information. This initial step was critical for their strategy.
- Encryption: All sensitive customer data was encrypted both during transmission and at rest using industry-standard encryption protocols. Consequently, this enhanced security.
- Access Control: Role-based access was implemented, ensuring that only relevant employees could access sensitive information. This step was vital for limiting exposure.
- User Education: The company held regular training sessions to educate employees on data security practices, emphasizing the importance of recognizing phishing attempts. This built awareness and vigilance.
Results
Within six months of implementing these DLP strategies, Innovate Tech reported a significant decrease in security incidents and improved compliance with industry regulations. As a direct result, customer trust increased, leading to a 30% growth in user engagement.
Conclusion
Implementing effective Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies is crucial for organizations seeking to protect sensitive data in today’s cyber landscape. By adopting a multi-faceted approach that includes data classification, encryption, access control, endpoint protection, user education, and incident response, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of data loss.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, staying proactive and adaptable in your DLP strategies will help ensure the integrity and security of your data. Investing in robust DLP measures not only protects your organization but also fosters trust among customers and stakeholders.
In conclusion, effective DLP strategies are not just a technical necessity—they are a fundamental component of a successful business strategy in the digital age. Start implementing these practices today to fortify your organization against potential data breaches and secure your path to success in an increasingly competitive environment.
FAQs about DLP Strategies
1. What types of data should be prioritized in a DLP strategy?
Organizations should prioritize sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, intellectual property, and health information. This focus is essential for effective protection.
How can small businesses afford DLP solutions?
Many DLP solutions offer scalable options suitable for different budgets. Additionally, cloud-based DLP services can significantly reduce upfront costs while providing robust protection. Thus, affordability is achievable for various organizations.
What are common mistakes in implementing DLP?
Common mistakes include insufficient employee training, lack of regular audits, and failing to adapt DLP strategies to evolving threats. Therefore, organizations should frequently reassess their DLP measures to ensure effectiveness.
How often should DLP strategies be reviewed?
DLP strategies should be reviewed at least annually or whenever significant changes occur in business operations or data regulations. Regular assessments help ensure that strategies remain effective and relevant.
Can DLP solutions integrate with existing security tools?
Yes, most DLP solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing security infrastructure, enhancing overall data protection efforts without requiring a complete overhaul of security systems. This compatibility is crucial for ensuring comprehensive security.

