
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring that applications and services are both scalable and reliable is paramount for businesses aiming to meet user expectations and maintain a competitive edge. Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) and DevOps development have emerged as pivotal disciplines that bridge the gap between development and operations, emphasizing automation, monitoring, and a culture of continuous improvement to achieve these goals.
By integrating principles of both Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) and DevOps development, organizations can build a strong foundation for delivering high-performing, resilient systems. This combined approach not only accelerates deployment cycles but also enhances system reliability, enabling teams to innovate quickly while maintaining operational stability and user trust.
The Essence of Site Reliability Engineering
Introduced by Google in 2003, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) applies software engineering principles to IT operations, aiming to create ultra-scalable and highly reliable software systems. By combining SRE practices with DevOps development strategies, organizations can build systems that are not only resilient but also agile and efficient. This approach focuses on both building robust systems and maintaining them effectively through automation and proactive practices.
Core Principles of SRE
To effectively implement SRE, organizations adhere to several foundational principles:
- Emphasize Reliability: Prioritizing system reliability ensures that services are consistently available and performant, directly impacting user satisfaction.
- Use Data to Drive Decisions: Making informed decisions based on metrics and data analysis helps in proactively identifying and addressing potential issues.
- Automate Everything: Reducing manual interventions through automation minimizes human error and increases operational efficiency.
- Work in Small, Iterative Steps: Implementing changes incrementally allows for easier troubleshooting and reduces the risk of significant system disruptions.
- Maintain Consistent, Reliable Environments: Ensuring uniformity across development, testing, and production environments helps in predicting system behavior accurately.
- Make Security a Top Priority: Integrating security practices into the development and operational processes safeguards systems against potential threats.
- Foster a Culture of Collaboration: Encouraging open communication and teamwork between development and operations fosters a shared responsibility for system health.
Key Practices in SRE
Beyond its principles, SRE encompasses specific practices that operationalize its philosophy:
Service Level Objectives (SLOs)
SLOs define the target level of reliability for a service, setting clear expectations for performance. They are crucial for aligning technical efforts with business goals and user expectations.
Error Budgets
An error budget quantifies the permissible amount of downtime or failures within a given period, balancing the need for innovation with reliability. For instance, if a service has a 99.9% availability SLO, it allows for approximately 43 minutes of downtime per month. This budget helps teams decide when to prioritize new feature development versus system stabilization efforts. When integrated with DevOps development workflows, error budgets serve as a shared accountability metric that aligns reliability goals with rapid delivery.
Error Budget Tracking Table (Sample)
| Day | Downtime (min) | Budget Used (%) | Remaining (%) |
| 1 | 0 | 0% | 100% |
| 10 | 15 | 34.9% | 65.1% |
| 20 | 30 | 69.8% | 30.2% |
| 30 | 45 | 104.7% | -4.7% |
Graph: Error Budget Consumption Over 30 Days
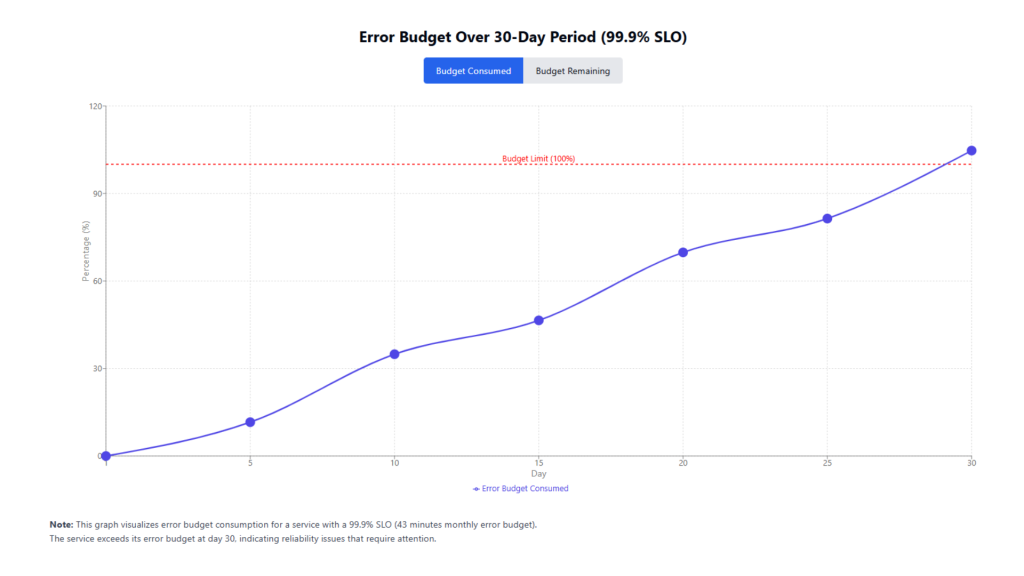
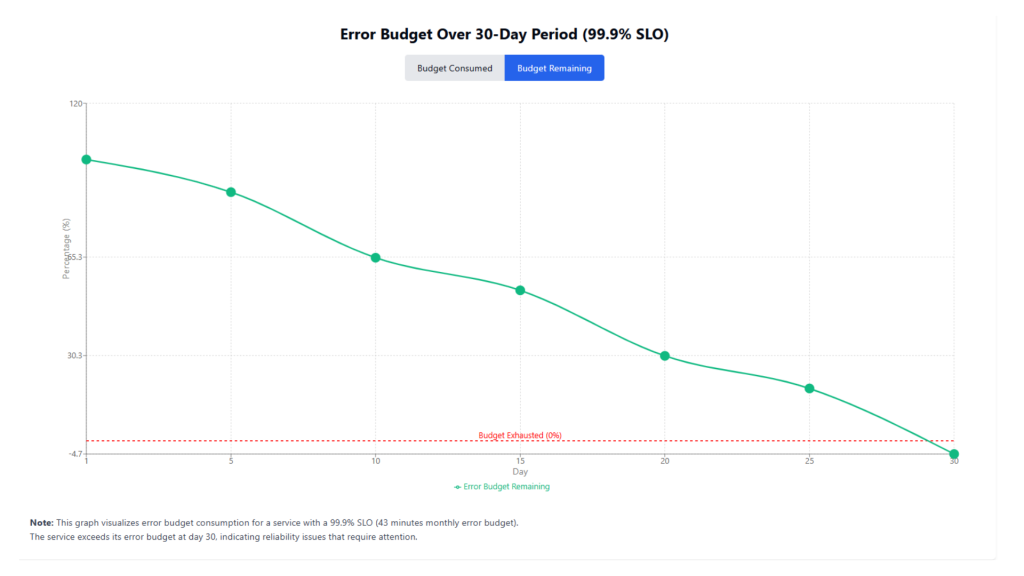
This graph provides visibility into how quickly reliability is consumed, helping engineering teams make smarter decisions regarding feature releases, operational planning, and long-term reliability—especially when balancing the pace of DevOps development with the principles of Site Reliability Engineering.
Toil Reduction
Toil refers to repetitive, manual tasks that are devoid of enduring value. SRE aims to minimize toil through automation, allowing engineers to focus on more strategic initiatives. Reducing toil not only enhances productivity but also improves job satisfaction among team members.
Monitoring and Observability
Implementing robust monitoring systems enables teams to detect anomalies and address issues proactively. Observability goes a step further by providing insights into the internal state of systems based on external outputs, facilitating deeper analysis and understanding.
Business Benefits of Adopting SRE
Integrating SRE practices offers organizations several tangible advantages:
- Enhanced System Reliability: Proactive monitoring and adherence to SLOs ensure higher uptime and consistent performance.
- Efficient Incident Management: Clear protocols and automation tools enable swift identification and resolution of issues, minimizing impact.
- Balanced Innovation and Stability: Error budgets provide a framework to manage the trade-off between deploying new features and maintaining system reliability.
- Scalable Operations: Automation and standardized practices facilitate seamless scaling of services to meet growing demands.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Reliable and performant services lead to a better user experience, fostering trust and loyalty.
SRE vs. DevOps: Clarifying the Distinction
While SRE and DevOps share common goals of enhancing collaboration and improving system reliability, they differ in focus and implementation. When combined, Site Reliability Engineering and DevOps development offer a powerful framework for delivering scalable, stable, and continuously evolving systems.
DevOps: Centers on fostering collaboration between development and operations teams to streamline software delivery and integrate continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices.
SRE: Emphasizes applying software engineering techniques to operational problems, with a strong focus on automation, reliability metrics, and system scalability.
In essence, DevOps is a cultural movement aimed at unifying development and operations, while SRE provides a set of practices and principles to achieve reliability within that framework.
While SRE and DevOps are tightly linked, they’re not interchangeable:
| DevOps | SRE |
| Cultural movement promoting collaboration between dev and ops | Engineering practice focused on reliability |
| Emphasizes CI/CD pipelines, automation, and fast releases | Uses metrics (SLOs, SLIs) and error budgets to manage risk |
| Broad and philosophical | Specific, measurable, and implementation-driven |
- In short: DevOps is the “why”, while SRE is the “how”—and together, they form the backbone of modern digital operations.
Applications of SRE in Real-World Scenarios
Site Reliability Engineering is not limited to tech giants anymore. Businesses across industries are adopting SRE and DevOps development practices to ensure the high availability, resilience, and agility of their systems. Here’s how SRE is being used in different contexts:
1. E-commerce Platforms
SRE practices help large-scale retail platforms ensure 24/7 uptime during high-traffic events like Black Friday. Through proactive monitoring and error budgeting, teams can respond rapidly to issues without customer-facing disruptions.
2. FinTech and Banking
Financial services rely heavily on system accuracy and availability. SRE enables real-time monitoring of critical transactions, ensures compliance through auditing, and reduces toil to keep operations lean and secure.
3. Healthcare Systems
In healthcare tech, where downtime can be life-threatening, SRE provides the tools to maintain service reliability, automate incident response, and uphold data integrity and security.
4. Streaming & Media
Companies like Netflix use SRE to manage complex microservices architectures, ensuring smooth video playback and uninterrupted service—even as user demand scales dynamically.
5. Cloud Providers and SaaS
SRE is central to cloud-native operations. It enables service providers to maintain agreed-upon SLOs across global regions, enforce redundancy, and roll out features safely.
Why SRE Is a Strategic Imperative
In an age where downtime equals lost revenue and user frustration, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) and DevOps development aren’t just technical choices—they’re business imperatives. By embedding reliability into the software development lifecycle, this combined approach empowers organizations to innovate without sacrificing stability.
The beauty of SRE lies in its balance—between speed and safety, autonomy and accountability, innovation and reliability. Whether you’re a startup or a large enterprise, adopting SRE principles alongside DevOps development is a step toward building not just better software, but stronger user trust and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary goal of Site Reliability Engineering?
The main objective of Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) is to ensure that systems are reliable, scalable, and efficient by applying software engineering practices to IT operations, supported by automation, monitoring, and performance metrics.
How is SRE different from DevOps development?
While both aim to enhance software delivery and reliability, DevOps is a cultural approach focused on collaboration and CI/CD, whereas SRE is a practical engineering implementation that uses tools like SLOs, SLIs, and error budgets to maintain system stability and performance.
Which industries are adopting SRE and DevOps development?
Originally introduced by Google, SRE is now widely adopted across industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and SaaS—anywhere reliability, scalability, and uptime are critical.
Is SRE suitable for small businesses or startups?
Yes. Smaller teams can successfully implement lightweight SRE practices like monitoring, basic automation, and error budgeting to increase efficiency and reliability without needing extensive resources.
How can an organization begin implementing SRE?
Start by defining measurable Service Level Objectives (SLOs) for your services, evaluate current performance, introduce automated alerting, and focus on reducing manual toil through smart automation. Integrating these with DevOps development practices accelerates both stability and delivery.

