In 2025, digital transformation drives every successful business. As organizations adopt dozens—sometimes hundreds—of applications, creating seamless, secure, and reliable connections between them becomes mission-critical. Relying on ad-hoc, one-off integrations leads to fragile, costly systems and data silos. Instead, Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIP) offer a blueprint for structured, maintainable, and future-ready connectivity.
This comprehensive guide explains what Enterprise Integration Patterns are, why they matter more than ever, how to use them effectively, and what best practices help enterprises thrive amid cloud, APIs, microservices, and ever-evolving technologies. Whether you are a CTO, architect, or team lead, you’ll discover practical, daily solutions to integration challenges—built with depth, clarity, and proven results.
What Are Enterprise Integration Patterns?
Enterprise Integration Patterns are standardized design approaches for moving, transforming, and managing data between independent systems or applications. Initially codified by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Woolf, these patterns form the language of modern integration—applicable in cloud, SaaS, APIs, legacy, and cutting-edge environments alike.
Instead of building fragile, point-to-point links, teams leverage EIP to ensure systems communicate robustly. Moreover, EIP supports reusability, scalability, and transparency—saving time and reducing risk as you scale up, migrate, or modernize.
Why Are Enterprise Integration Patterns Essential Now?
Nearly every organization faces rapid cloud adoption, real-time workflows, complex data regulations, and hybrid environments. Consequently, integration is no longer just an IT concern—it’s a business necessity. EIP lets you adapt to tomorrow’s requirements, not just today’s needs.
Key Benefits of Enterprise Integration Patterns
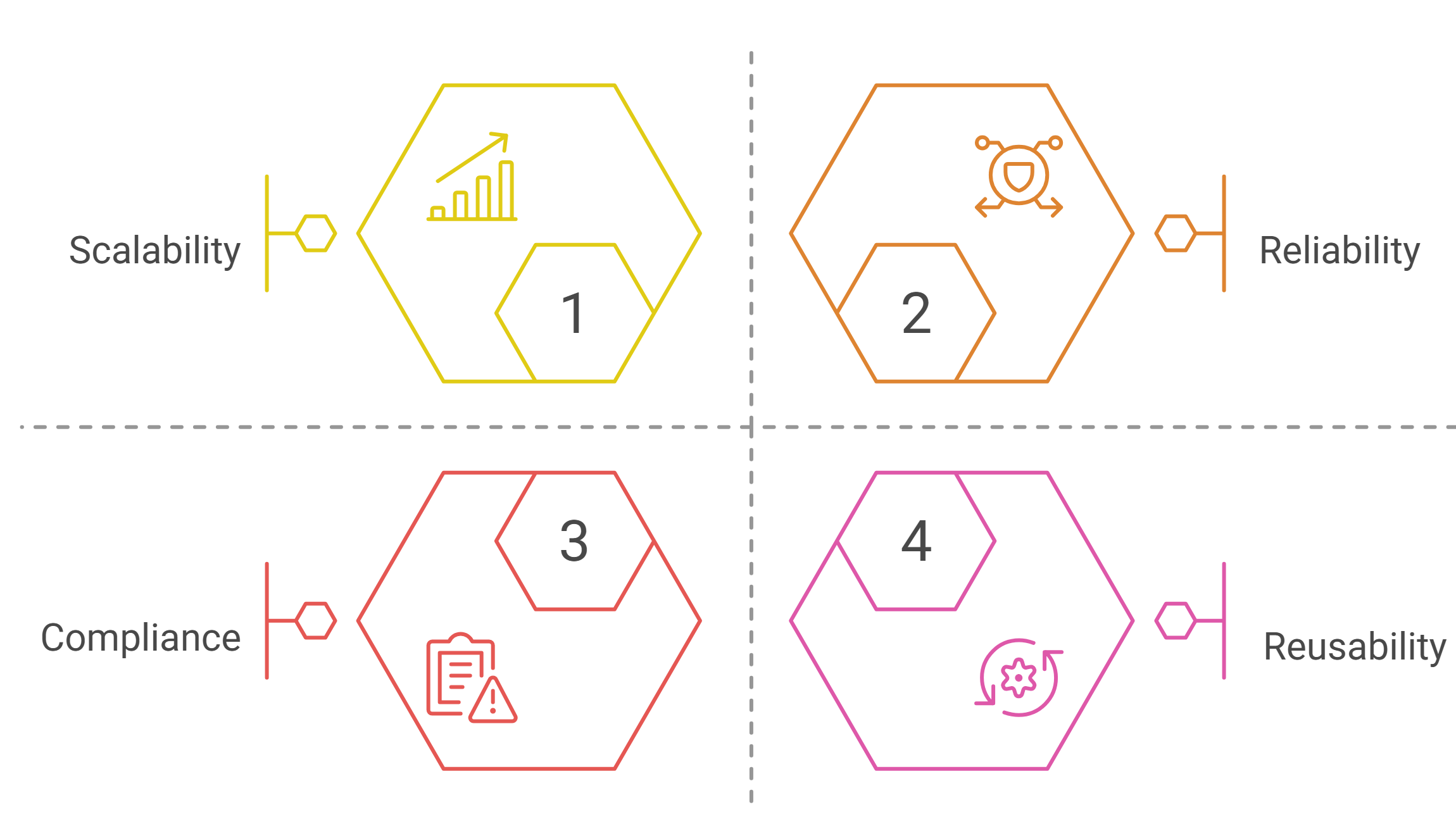
1. Scalability and Flexibility
By decoupling systems, you can swap, add, or upgrade applications with minimal rework. This agility gives enterprises a genuine competitive edge.
2. Greater Reliability
EIP ensures messages flow even if parts of your system go offline. Patterns such as Guaranteed Delivery and Dead Letter Channels allow you to spot, fix, and review any issues instantly.
3. Improved Compliance
Centralizing integrations lets you log, trace, and audit every data exchange—making it easier to meet requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX.
4. Reusability and Speed
Rather than reinventing the wheel, you can reuse tested patterns across teams and projects. This reduces bugs, saves time, and accelerates delivery.
Core Enterprise Integration Patterns Explained
Let’s explore the most used Enterprise Integration Patterns, each illustrated with modern business scenarios and crisp, transition-rich explanations.
1. Message Channel
All communications happen through named, logical channels. One system “publishes” messages; others “subscribe” to receive them. Consequently, direct connections and dependencies are minimized.
Example:
A retail application publishes order confirmations to a message channel. Warehouse, finance, and shipping systems subscribe—reacting automatically to new orders.
2. Message Translator
Since different systems speak different data languages, the Message Translator converts one format into another. Thus, legacy applications and cloud solutions can communicate seamlessly.
Modern Usage:
A finance system exports invoices as XML, but a cloud reporting platform reads JSON. The translator bridges the gap—converting and validating both ways.
3. Content Enricher
Sometimes a message needs extra information to be processed. The Content Enricher pattern calls external services or databases to supplement the message before passing it on.
Scenario:
An online order arrives without customer tier information. The Content Enricher queries the CRM and appends loyalty status for personalized handling.
4. Content Filter
To avoid exposing unnecessary data, the Content Filter shrinks messages to only the required fields. This reduces bandwidth, security risk, and compliance headaches.
Example:
Before sending transaction logs to a third-party analytics tool, the Content Filter removes personal financial data.
5. Splitter and Aggregator
Complex messages, such as multi-item purchase orders, are split into individual messages (Splitter), processed separately, and later combined (Aggregator) into a unified result.
Daily Use Case:
A shipment API splits an order into individual items, sends each for fulfillment, then aggregates shipment statuses for customer notifications.
6. Routing Patterns
These patterns decide where each message should go—based on rules, message content, or system health.
- Content-Based Router: Directs messages depending on content, e.g., international orders to one platform, local to another.
- Recipient List: Sends the same message to multiple endpoints, e.g., alerts to management, operations, and compliance teams.
- Dynamic Router: Routes messages “on the fly,” supporting rapidly scaling microservices or partner lists.
7. Error Handling and Reliability
No integration is perfect. These patterns keep your business running smoothly:
- Dead Letter Channel: Stores failed messages for analysis and reprocessing.
- Retry: Automatically attempts to resend failed messages after delays.
- Circuit Breaker: Prevents systems from being overwhelmed during major outages by rerouting or stopping message flow temporarily.
Why it matters:
When one partner’s endpoint fails, you don’t lose important data. Instead, errors are logged, retried, and escalated only as needed.
8. Process Manager (Saga)
For multi-step, long-running processes that require orchestration and compensation, the Process Manager pattern keeps track. If a step fails, compensating actions are triggered automatically.
Real-World Example:
In supply chain automation, a failed item procurement triggers reverse transactions for payment and inventory, maintaining consistency.
Real-World Scenarios for Enterprise Integration Patterns
Scenario 1:
A global logistics company uses EIP for seamless integration across customs, warehouse, insurance, and delivery partners. Adoption of Content-Based Routing and Aggregator patterns allows automatic re-routing during disruptions, rapid error recovery, and a unified customer experience.
Scenario 2:
A healthcare provider complies with HIPAA through Content Filtering and Message Translator patterns, ensuring sensitive health data is masked before transmitting data to analytics and research partners.
Scenario 3:
A fintech startup uses Dead Letter Channels and Process Managers within API-driven microservices, making sure failed transactions are never lost and system workflows self-heal after issues.
Implementing Enterprise Integration Patterns in 2025
Modern Tools and Approaches
- Apache Camel: A flexible framework supporting all major EIP, popular in Java and Spring Boot ecosystems.
- Spring Integration: Seamless for Spring applications, supporting pattern composition and cloud-native deployments.
- Enterprise iPaaS (Dell Boomi, MuleSoft): Visual “low code” platforms putting EIP power in the hands of non-developer business analysts.
- Cloud Platforms (AWS Step Functions, Azure Logic Apps, Google Workflows): Built-in workflow engines and pattern support for scalable, event-driven integrations.
Steps for Successful Implementation
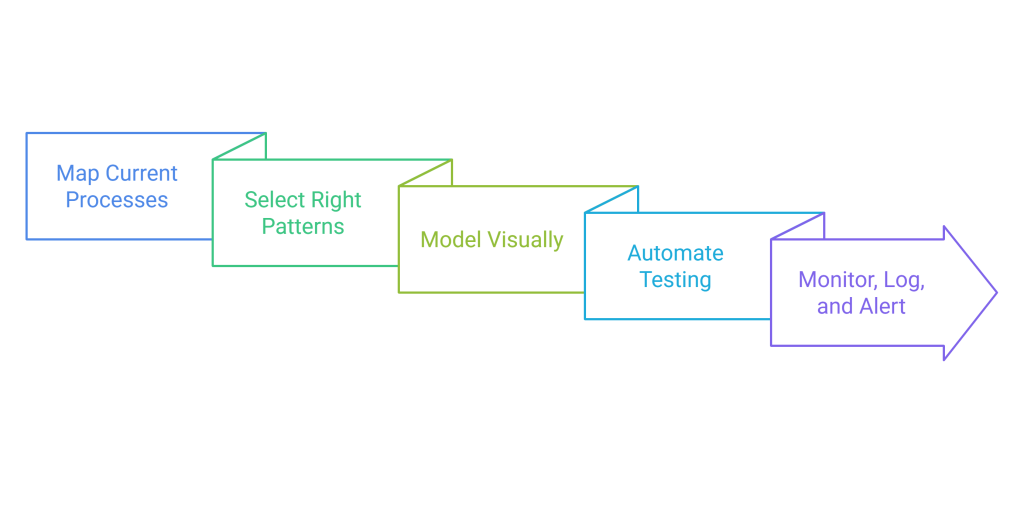
- Map Current Processes: Document every data flow, integration point, and business requirement.
- Select the Right Patterns: Match each connection to the appropriate EIP, considering reliability, compliance, and scaling needs.
- Model Visually: Use diagrams and flowcharts for clear communication across business and IT teams.
- Automate Testing: Invest in robust integration and regression testing as part of your CI/CD pipelines.
- Monitor, Log, and Alert: Make integration fully observable; respond to issues before users notice them.
Advanced Trends Shaping Enterprise Integration Patterns
Event-Driven Architectures
Increasingly, businesses require real-time reactions. EIP are foundational for event-driven approaches, making sure messages flow instantly across workflows, from sales triggers to IoT alerting.
Hybrid, API-First, and Serverless Integrations
Modern enterprises blend cloud APIs, traditional systems, and serverless functions—EIP ensures consistent connections, asynchronous processing, and secure message handling everywhere.
AI-Enhanced Middleware
AI-powered integration platforms now optimize routing, detect anomalies, and suggest fixes—making daily management smarter and more autonomous.
Security and Compliance Automation
EIP supports centralized controls for filtering, masking, logging, and encrypting messages, thus simplifying GDPR, CCPA, and SOX compliance as regulations expand.
Daily Best Practices for Enterprise Integration Patterns
- Educate Everyone: Hold regular team workshops and code reviews highlighting EIP usage and anti-patterns.
- Document Flows: Always keep integration diagrams and message schemas current.
- Automate Deployments: Use CI/CD pipelines for all integration changes, including testing and rollback.
- Design for Failure: Expect connections to drop; use error handling and retry patterns religiously.
- Monitor Everything: Track latency, errors, and message volumes; respond to alerts quickly.
- Start Simple: Gradually replace legacy integrations with EIP-based solutions to reduce risk.
- Prioritize Security: Combine content filtering, encryption, and audit logging in every integration.
Conclusion
Modern business success hinges on smart, sustainable integration. By adopting Enterprise Integration Patterns, you ensure every system communicates cleanly, every workflow stays resilient, and your architecture scales with future demands. Whether connecting microservices, automating supply chains, or enabling cloud migration, EIP are your blueprint for reliable, compliant, and efficient connectivity in 2025 and beyond.
Invest in EIP today—unlocking the potential of every application, every process, and every team in your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why should businesses embrace Enterprise Integration Patterns?
Without EIP, integration projects become tangled, fragile, and expensive. EIP makes systems scalable, resilient, and easier to change—crucial for growth and compliance.
How do EIP fit into microservice and API architectures?
EIP is even more vital for microservices, which require loose coupling, reliable communication, and error handling. EIP patterns prevent “spaghetti” code and enable manageable scaling.
Can small companies benefit from Enterprise Integration Patterns?
Absolutely. Even startups with limited systems gain stability, speed, and clarity by adopting core EIP for their internal tools, SaaS, and partner integrations.
Are Enterprise Integration Patterns relevant in serverless or cloud-native apps?
Yes! Cloud services and serverless architectures often depend on messaging and event-based flows—EIP ensures your approach is robust, auditable, and future-proof.
Should EIP be managed within code or iPaaS?
Use the best fit for your team and needs: code-based frameworks for developer teams, or iPaaS for business-driven, low-code integrations. What matters most is clear use of the patterns, not how they’re implemented.

