
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cross-platform app development has become a cornerstone for businesses aiming to reach wider audiences efficiently. Instead of creating separate native apps for each operating system, developers now craft apps that work seamlessly across Android, iOS, and even web platforms. This approach not only reduces development time and costs but also simplifies maintenance and updates.
However, with this convenience comes a crucial responsibility: ensuring security across all platforms. As apps become more complex and handle increasing volumes of sensitive data, the risks of vulnerabilities and cyberattacks escalate. Hence, security-first cross-platform app development is not just a recommendation but a necessity.
This blog delves into the essential security aspects of cross-platform development, focusing on encryption techniques, Identity and Access Management (IAM), and adherence to the OWASP guidelines. By adopting these strategies, developers can build robust apps that protect users’ data and maintain trust in an increasingly security-conscious world.
Understanding Cross-Platform App Developmen
At its core, cross-platform app development is a methodology where a single codebase is used to create applications that run on multiple operating systems. This contrasts with native app development, which requires building separate apps for Android, iOS, and other platforms using platform-specific languages like Java or Swift.
Advantages of Cross-Platform Development
- Cost Efficiency: Since developers write one codebase, the overall development and maintenance costs drop significantly.
- Faster Time to Market: Simultaneous deployment across platforms accelerates app release cycles.
- Unified User Experience: Consistent UI/UX design ensures a similar feel, regardless of the platform.
- Easier Maintenance: Updates and bug fixes can be deployed across all platforms simultaneously.
- Larger Reach: Businesses can target a wider audience without doubling the development effort.
Disadvantages and Challenges
However, cross-platform development is not without its drawbacks:
- Performance Limitations: Native apps often outperform cross-platform apps in speed and responsiveness due to direct hardware access.
- Platform-Specific Features: Some advanced features may be harder to implement or may require platform-specific adjustments.
- Security Concerns: Different platforms have varying security protocols, which can complicate uniform security enforcement.
Popular Frameworks and Tools
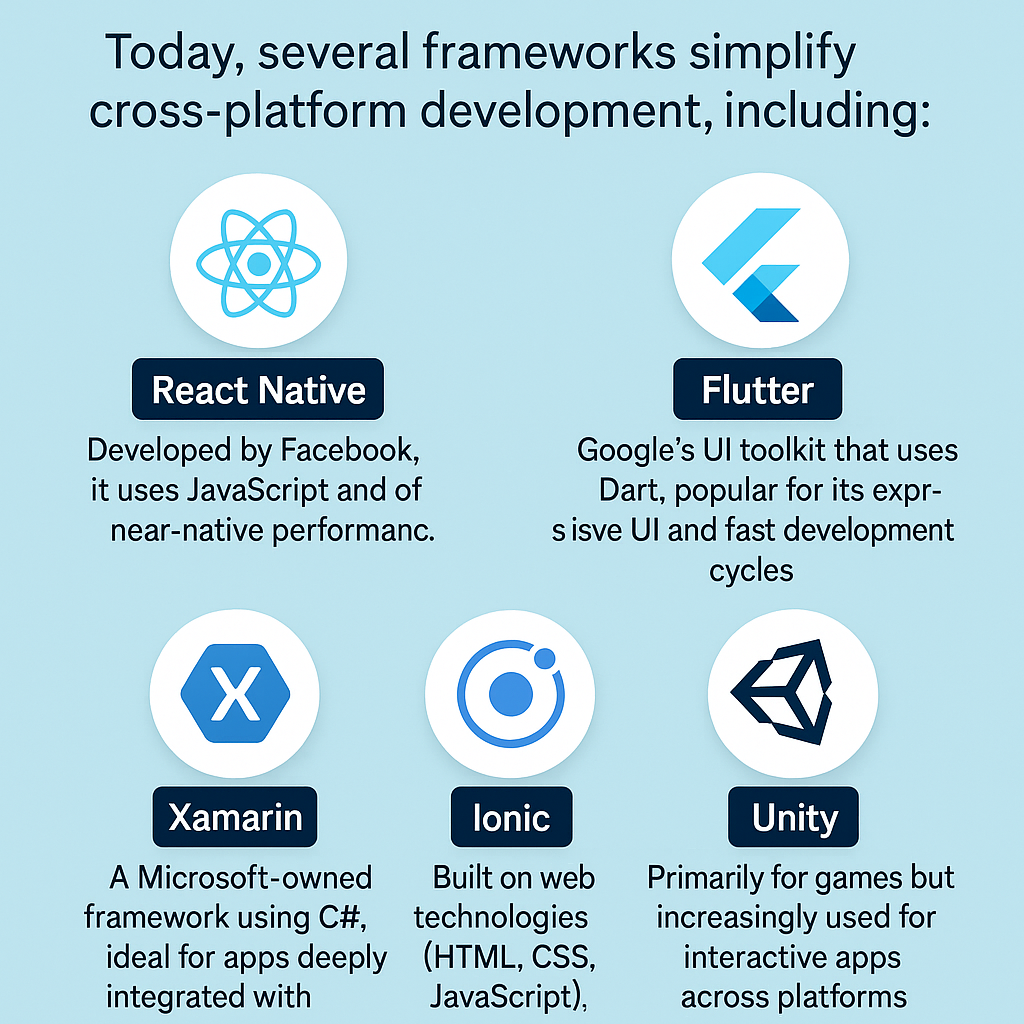
Today, several frameworks simplify cross-platform development, including:
- React Native: Developed by Facebook, it uses JavaScript and offers near-native performance.
- Flutter: Google’s UI toolkit that uses Dart, popular for its expressive UI and fast development cycles.
- Xamarin: A Microsoft-owned framework using C#, ideal for apps deeply integrated with Microsoft ecosystems.
- Ionic: Built on web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), focusing on hybrid apps.
- Unity: Primarily for games but increasingly used for interactive apps across platforms.
Trends in Cross-Platform Development
According to a recent report by Statista, the cross-platform development market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18% over the next five years, underscoring its rising popularity. Furthermore, advancements in frameworks are closing the performance gap with native apps, encouraging more developers to adopt cross-platform strategies.
The Security Imperative
Despite the numerous benefits, security is often an afterthought in cross-platform development — a costly mistake in today’s threat landscape.
Why Security Must Be a Priority
With the surge in mobile and web app usage, malicious actors are increasingly targeting these platforms. Breaches can expose user data such as personal information, financial details, and login credentials, leading to severe consequences including financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
Moreover, apps today frequently integrate with third-party services, cloud platforms, and APIs, exponentially increasing the attack surface. In cross-platform environments, this complexity is heightened since each platform might have distinct vulnerabilities and security features.
Common Security Threats for Cross-Platform Apps
- Data Leakage: Sensitive data inadvertently exposed via logs, caches, or local storage.
- Insecure Communication: Unencrypted data transmissions vulnerable to interception.
- Authentication Flaws: Weak or missing authentication allowing unauthorized access.
- Insecure Code Practices: Usage of outdated libraries, lack of input validation leading to injection attacks.
- Improper Session Management: Sessions not properly secured or terminated.
- Platform-Specific Vulnerabilities: Each OS may have unique security quirks needing tailored protections.
Consequently, adopting a security-first mindset means embedding security throughout the app development lifecycle rather than retrofitting it at the end.
Encryption in Cross-Platform Development
What Is Encryption and Why Is It Important?
Encryption transforms readable data into an unreadable format using algorithms, making it accessible only to authorized parties with decryption keys. In cross-platform apps, encryption is vital to protect sensitive user data — whether stored locally on devices or transmitted over networks.
Encryption ensures confidentiality, integrity, and often authenticity of data. Without it, information like passwords, credit card details, or personal messages become vulnerable to theft or tampering.
Encryption Methods Used in Apps
There are various encryption algorithms and standards, each serving different purposes:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): A symmetric key algorithm widely used for encrypting stored data and communication streams. AES is efficient and secure when properly implemented.
- RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman): An asymmetric encryption algorithm using public/private key pairs, often employed to securely exchange symmetric keys or for digital signatures.
- TLS (Transport Layer Security): A protocol ensuring encrypted communication over networks, essential for HTTPS connections.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): Encrypts data at the source and decrypts only at the destination, preventing intermediaries from accessing the plaintext.
Implementing Encryption in Secure Cross-Platform Apps
Implementing encryption requires careful consideration of platform differences:
- Local Data Encryption: Use platform-agnostic libraries like libsodium or framework-specific plugins for encrypting files or databases on the device.
- Secure Communication: Always employ TLS/SSL for network communication, ensuring API calls and data transfers are encrypted.
- Key Management: Keys must never be hardcoded or stored insecurely. Utilize secure storage mechanisms such as Keychain on iOS and Keystore on Android.
- End-to-End Encryption: For messaging or sensitive transactions, incorporate E2EE protocols using well-established libraries.
Practical Example
For instance, a Flutter app can leverage the flutter_secure_storage plugin to securely store encryption keys on both iOS and Android devices, ensuring that sensitive keys are protected from unauthorized access.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Defining IAM and Its Role
IAM is a comprehensive framework that manages digital identities and controls user access to resources. In cross-platform apps, IAM ensures that only authorized users can perform specific actions, protecting sensitive functionalities and data.
Core Components of IAM
- Authentication: Verifying user identity via passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Authorization: Defining and enforcing permissions to access resources based on user roles or attributes.
- User Management: Creating, updating, and deleting user profiles securely.
Best Practices for IAM in Cross-Platform Apps
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Combining something users know (password) with something they have (OTP) or are (biometrics) significantly improves security.
- Adopt OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect: These protocols standardize secure user authentication and authorization, especially when integrating third-party identity providers like Google or Facebook.
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on user roles to limit access.
- Secure Session Management: Use short-lived tokens, refresh mechanisms, and secure cookies.
- Centralize IAM Logic: Where possible, handle IAM on backend servers or cloud identity platforms to minimize exposure on client devices.
IAM Tools and Technologies
- Firebase Authentication: Popular for mobile apps, providing ready-made authentication services with secure token management.
- Auth0: A flexible identity management platform supporting many authentication protocols.
- AWS Cognito: Amazon’s cloud service for user authentication and access control, suitable for scalable apps.
By integrating robust IAM, developers can safeguard user identities while simplifying access control in cross-platform environments.
Adhering to OWASP Guidelines
What is OWASP?
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a nonprofit organization dedicated to improving software security. It provides widely recognized resources like the OWASP Top Ten, a list of the most critical security risks for web and mobile applications.
Key OWASP Guidelines Relevant to Cross-Platform Apps
The OWASP Top Ten includes vulnerabilities such as:
- Injection Flaws (e.g., SQL, NoSQL injection)
- Broken Authentication
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- XML External Entities (XXE)
- Broken Access Control
- Security Misconfiguration
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Insecure Deserialization
- Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- Insufficient Logging & Monitoring
Integrating OWASP Guidelines into Development
To mitigate these risks:
- Validate and Sanitize Input: Prevent injection and XSS attacks by validating all user inputs.
- Implement Strong Authentication and Session Controls: Protect user credentials and session tokens.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Both in transit and at rest.
- Keep Dependencies Updated: Regularly update third-party libraries to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Harden Configurations: Disable unnecessary features and ensure secure defaults.
- Perform Regular Security Testing: Conduct static code analysis, penetration testing, and dynamic scans.
By embedding these practices into the development lifecycle, teams can substantially reduce vulnerabilities in cross-platform apps.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of Security in a Cross-Platform App
Consider a fintech startup developing a budgeting app using React Native. Early in development, the team adopted a security-first approach:
- Encryption: All user data stored locally was encrypted with AES-256 using platform-specific secure storage.
- IAM: They implemented OAuth 2.0 authentication combined with biometric login support for enhanced security.
- OWASP Compliance: The app underwent rigorous code reviews and penetration testing aligned with OWASP standards.
Challenges
- Integrating biometric authentication consistently across Android and iOS required custom native modules.
- Ensuring encrypted communication with banking APIs demanded strict TLS configurations.
- Managing session expiration and token refresh logic across platforms introduced complexity.
Solutions and Outcomes
- The team leveraged third-party SDKs and libraries verified for security compliance.
- They established automated security testing in their CI/CD pipeline.
- As a result, the app launched with strong user trust, zero reported security incidents in the first year, and compliance with industry regulations like GDPR.
Conclusion
In conclusion, security-first cross-platform app development is essential in today’s technology environment. By leveraging strong encryption, implementing robust Identity and Access Management (IAM), and adhering to OWASP guidelines, developers can build applications that not only perform well across platforms but also protect user data and maintain trust.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, embracing a security-first mindset will differentiate successful apps from vulnerable ones. Ultimately, integrating these security practices from the outset enhances app reliability, user confidence, and compliance with regulations—making it a win-win for businesses and users alike.
FAQs
1. What is cross-platform app development?
Cross-platform app development involves creating software applications that run on multiple operating systems (like Android and iOS) from a single codebase, saving time and resources.
2. Why is security crucial in app development?
Apps handle sensitive user data and often connect to backend services. Without strong security, apps are vulnerable to breaches that can cause financial loss and damage reputations.
3. How can encryption enhance app security?
Encryption protects data by converting it into unreadable formats, ensuring that even if data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it cannot be understood or misused.

